
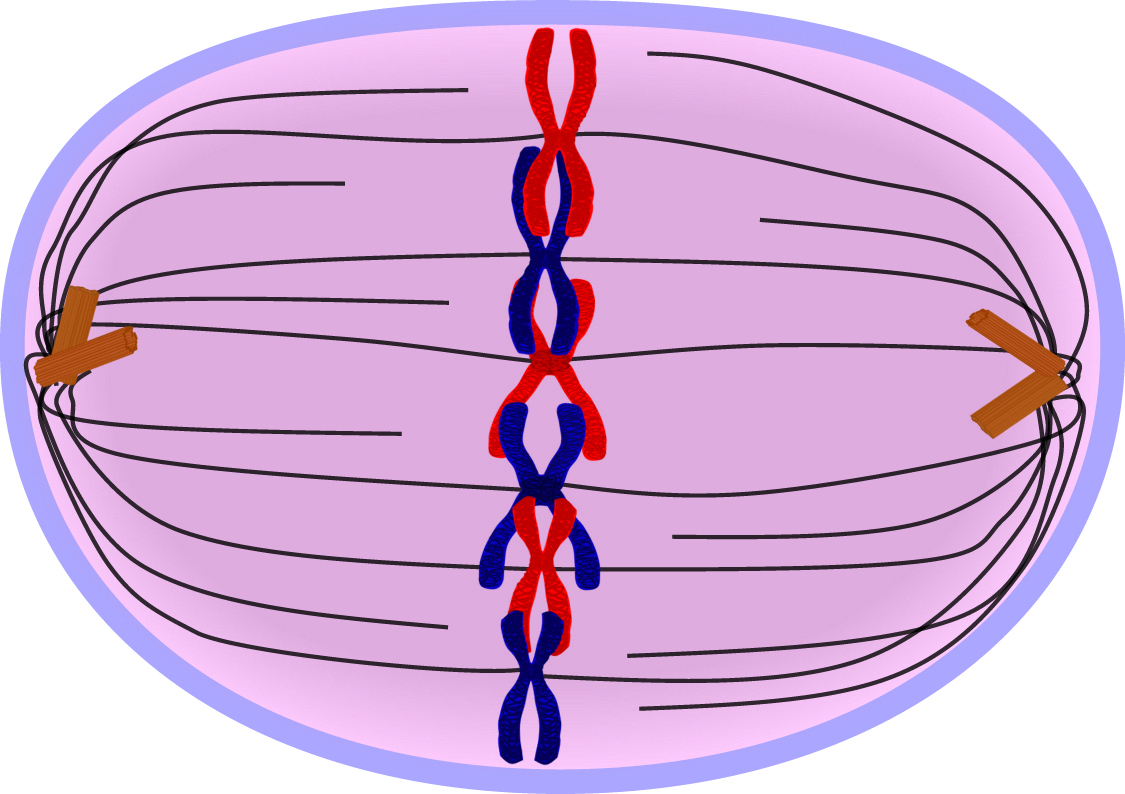

Mitosis can be further subdivided into four main phases: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase ( PPMAT). The movement of chromosomes is orchestrated by specialised structures called microtubules.
#Prophase definition biology series
The mitotic phase describes a series of processes during which the replicated DNA condenses into visible chromosomes, which are aligned, separated, and passed on to two new daughter cells. During this time, the cell undergoes additional growth, replenishes energy stores and prepares and reorganises the cytoplasmic components for division, including duplicating some organelles and dismantling the cytoskeleton. The final phase of interphase is the G2 phase. A centromere is a specialised sequence of DNA that links the sister chromatids and is important throughout mitosis. These sister chromatids are attached to each other by a centromere. This process of replication generates sister chromatids, which are identical pairs of chromosomes. S phaseĭuring the S phase, all the genetic information in the cell is copied by the process of DNA replication. The cell usually grows larger, and some organelles are copied. During G1, the cell is preparing to replicate DNA by synthesising the mRNAs and proteins required to execute the future steps. The first phase of interphase and the cell cycle is called G1. Checkpoints also exist at these phases to ensure the cell is ready to divide. The ‘ G’ phases (also called gap phases) represent periods of growth in preparation for the division of the cell. DNA replication occurs in the ‘ S’ phase (the ‘ Synthesis’ phase).

Interphase can be further subdivided into three phases: G1, S and G2. Most of the time in the cell cycle is spent in a preliminary phase: interphase. A typical human cell cycle takes around 24 hours, but the cell cycle can be drastically different in different cell type. During interphase, the cell grows and DNA is replicated, and during the mitotic phase, the cell divides and the DNA is distributed to the daughter cells. These events are tightly regulated and precisely timed, and can be grouped into two phases: interphase and the mitotic (M) p hase. The cell cycle describes a sequence of reactions that results in the growth of the cell and replication of the genetic material to make two identical daughter cells. During the final stages of the cell cycle, cytokinesis occurs, where the cytoplasmic contents are separated into two daughter cells.During these phases, the nuclear envelope disappears, the mitotic spindle forms, chromosomes condense and are lined up at the metaphase plate, and separated by being pulled to each side of the cell Mitosis encompasses prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase telophase.Interphase encompasses 3 phases: G1, S and G2.During interphase, cells are duplicating their material and synthesising proteins to prepare to divide.The cell cycle is made up of two main stages: interphase and mitosis.When does the duplication of DNA happen in interphase?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
